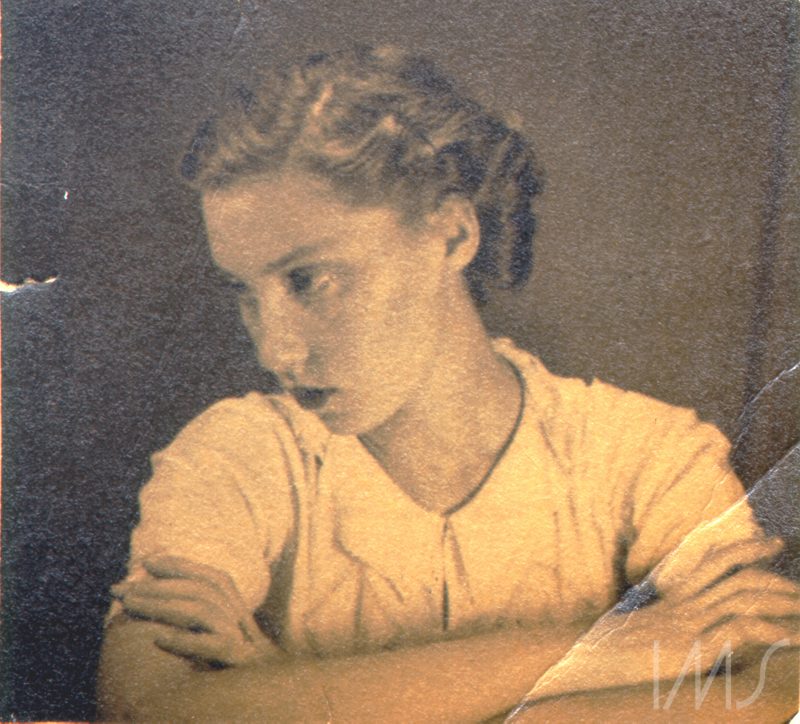, “The Chandelier” is published in English. IMS Clarice Lispector, 2018. Disponível em: https://site.claricelispector.ims.com.br/en/2018/04/05/o-lustre-e-publicado-em-ingles/. Acesso em: 27 July 2024.
The Chandelier, Clarice Lispector’s second novel, published in 1946, was just translated into English by Benjamin Moser and Magdalena Edwards. The book is another of a series of translations of the author’s works that have been published in the past few years. In a statement to The New York Times, Moser observes that this may be the strangest and hardest book by the Brazilian writer (who was born in Ukraine in 1920). The British critic Christopher Ricks, for his part, sees it as a miniature of Clarice’s universe:
So many of the themes, philosophical inquiries and character types that appear [in The Chandelier] will return, honed as Lispector refines her style and hardens them into the diamond like perfection of her final books, which are narrated in jagged aphorisms – ‘anti literature’ she called them.
The American newspaper furthermore celebrates the rediscovery of Clarice in the United States as one of the true literary events of the 21st century, highlighting the singularity of her writing, which is marked by a unique punctuation and syntax, in addition to a capacity to resignify words according to her own wishes – “No one sounds like Lispector (…). No one thinks like her,” the journalist Parul Sehgal concludes.
A few days after the American newspaper featured The Chandelier, the editor Gregory Cowles included the book on the list of ten reading suggestions that he made for the prestigious Book Review column.
Read The New York Times article here.
*Photo: Unidentified photographer/ Clarice Lispector Collection/ IMS